Many people consider RAID 6 the best option for choosing a RAID drive for data security. It offers high fault tolerance against drive failure and data loss. However, like other RAID arrays, RAID 6 uses a dedicated hardware controller to calculate the parity data and write data on all the disks. Being such an important component of the RAID 6 array, the entire array may become inaccessible if it fails, putting your data at great risk.
What is a RAID Controller and Why Does it Fail?
RAID controller could be a hardware component or software program that manages the number of disks to be added to the RAID array, the block sizes, and data storage. It offers a level of abstraction (defining how data will be stored, viewed, and related) between the RAID and the operating system.
These RAID controllers may fail for many reasons, including power outages, power surges, logical damage, drive component burn, component malfunctioning, and firmware issues. Other than these, improper RAID rebuilding, broken server connections, and server crashes may also cause RAID controller failure.
Another thing to consider is that multiple disk failures can also lead to controller failure. When more than one drive is severely damaged in the RAID array (depending on the specific RAID configuration), the chances of controller failure may increase.
Since the controller manages the disks in a RAID array and looks after data integrity with redundancy, multiple disk failures can put the Controller under great strain to maintain data availability and recovery, eventually leading to complete controller failure.
What Happens if RAID 6 Controller Fails?
When the Controller fails, the RAID 6 level may become inaccessible. Even if there is no damage to your disk platter or head and data is intact, you may be unable to view or access the RAID 6 array. However, as discussed above, it depends on the RAID configuration. For example, RAID 10 requires at least four drives to be configured and offers two drives’ fault tolerance, similar to RAID 6. This means that when one drive fails, the inherent redundancy will automatically retrieve data within the controller. However, if two drives fail, you can restore data using the RAID recovery tool.
How to Recover Data from RAID 6 after Controller Failure
Irrespective of how the RAID 6 controller failed in the first place, data recovery is still possible. This RAID array offers a maximum of two drives’ fault tolerance, meaning even if two drives fail in the array, the data can still be recovered with a powerful RAID data recovery tool, such as Stellar Data Recovery Technician. This DIY software supports recovery from RAID 0, 1, 5, and nested RAIDs, including RAID 10, 50, and 60. You can virtually rebuild RAID 6 after controller failure with the following steps to perform data recovery.
- Connect RAID 6 to your system.
- Download and runStellar Data Recovery Technician.
- On the initial screen,Select What to Recover, choose All Data, and clickNext.
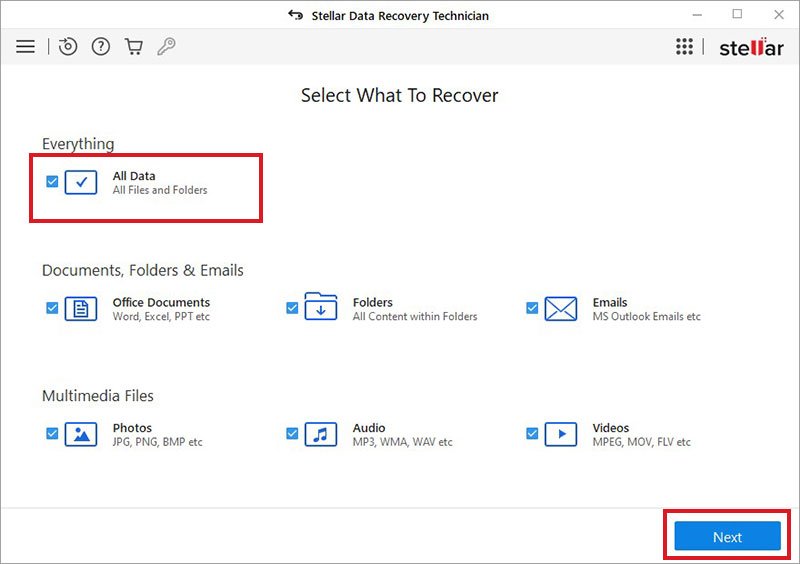
- Then, selectRaid Recoveryon the ‘Recover from’screen and clickScan.
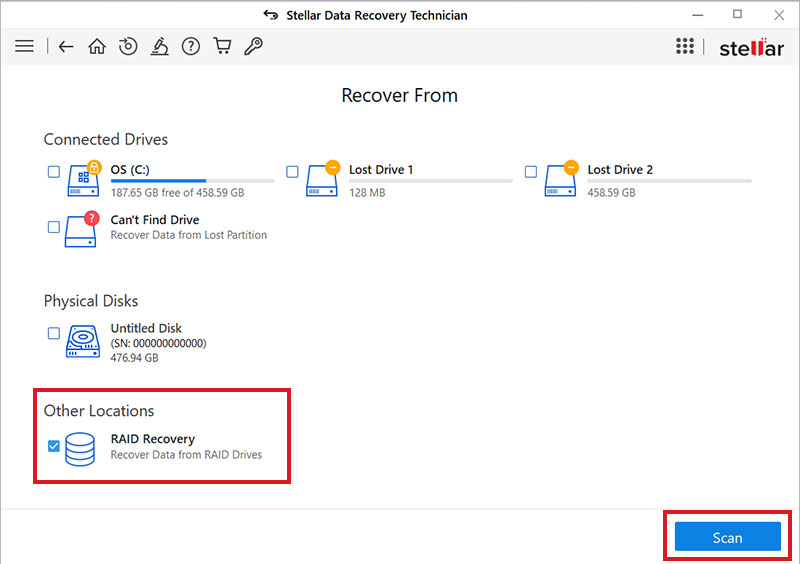
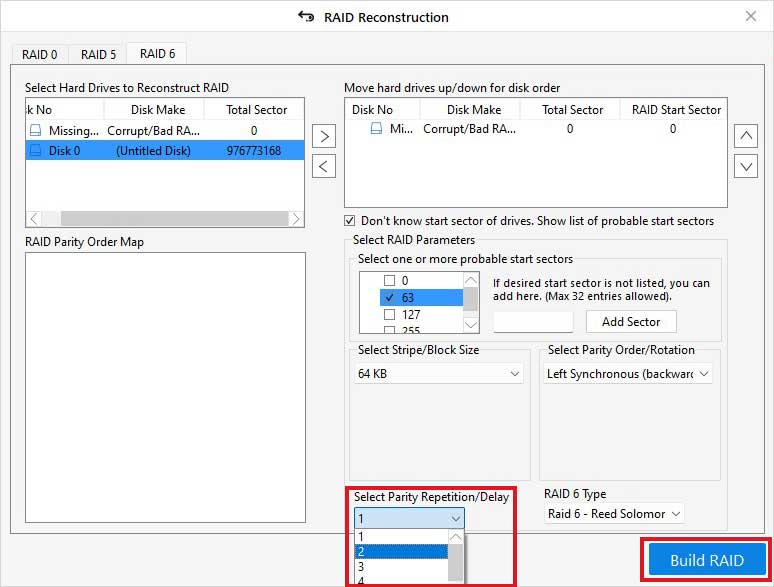
- Now, go to the'RAID 6' section and select the RAID 6 disks, and click'>'to move the disks in the'Move hard drives up/down for disk order' section.
- Afterward, move the disks Up/Down and finally place the disks in order.
- Further, choose parameters: RAID 6 Type from the drop-down menus, Stripe/Block Size, Parity Order/Rotation method, Parity Repetition/Delay time.
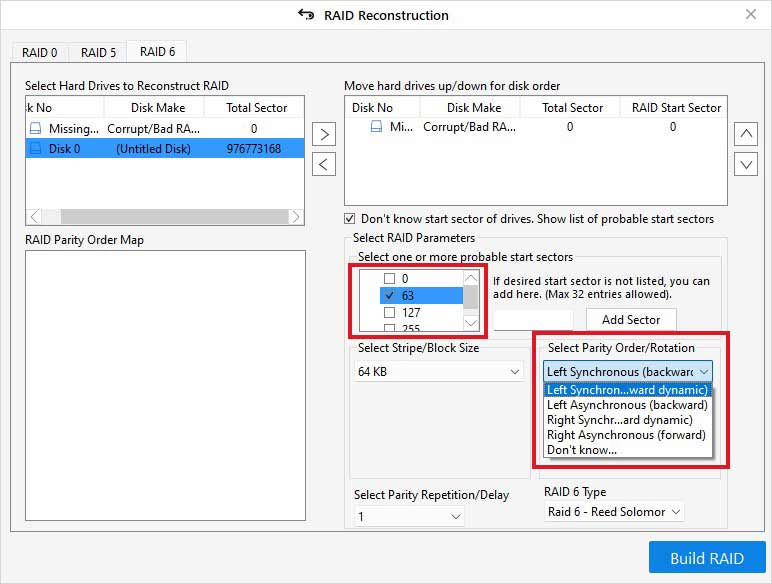
- Click theBuild RAIDoption.
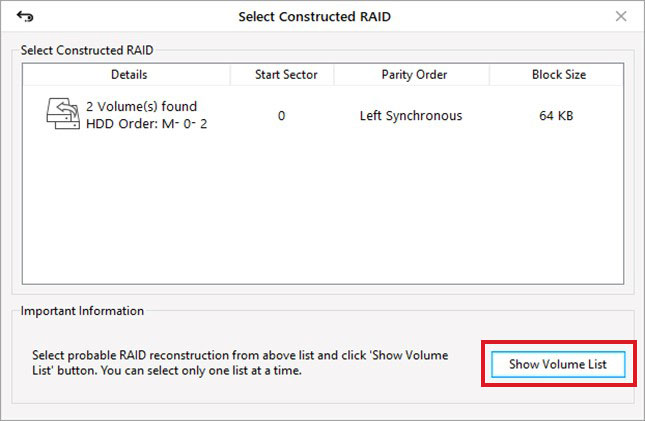
- On the nextSelect Constructed RAIDwindow, a single RAID 6 will appear.
- ClickShow Volume Listafter selecting RAID 6.
- SelectRAID volumeand clickScan.
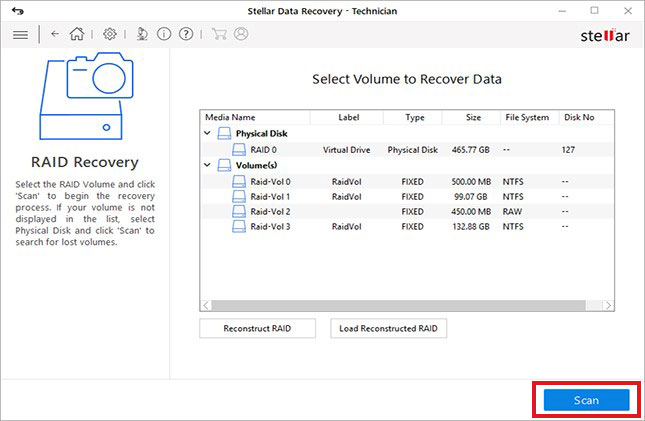
- After scanning, select the files/folders you want to retrieve and clickRecover.
- Finally, clickBrowseand thenStart-Savingto store the recovered data.
RAID 6 consumes less storage than RAID 10 (RAID 1+0), which only uses its half capacity in storing data and half in mirroring data on other connected drives in the array. This RAID array is best for long data retention environments, such as archiving. Although it offers better data security with dual parity, it can still fail or become inaccessible due to controller malfunctioning, outdated controller firmware updates, physical damage, and putting data at stake. Using anadvanced RAID data recovery tool, you can regain up to 100% of your data from RAID 6 after a controller failure.
FAQ
1. How many failures can RAID 6 tolerate?
RAID 6 follows dual parity, dividing the data across the disks in the array and building a combination of striped data. It can withstand up to two drive failures. However, if more than two drives fail, the RAID 6 array and data will be lost.
2. How long does it take to rebuild RAID 6 manually?
Manually rebuilding RAID 6 may take up from days to months. Additionally, there is a great risk of errors in manually rebuilding the RAID array. Hence, we recommend you opt for an automated way – RAID recovery software to rebuild failed RAID 6.
3. How many disks for RAID 6 are required?
A minimum of four drives are required for building a RAID 6 array. A maximum of 32 drives can be added to the array.